Our Technology
Electrospinning is
Electrospinning is a fiber production method that employs electric force to draw
charged jets of polymer solutions or polymer melts. The diameters of these jets
are generally in the order of some hundred nanometers. When an external electrostatic
field is applied to a conductive fluid, for example a spinning solution, a suspended
conical droplet, which is called Taylor cone, is formed.
Electrospinning occurs
when the electrostatic field is strong enough to overcome the surface tension of
the liquid. The liquid droplet then becomes unstable and a tiny jet is ejected from
the surface of the droplet. The ejected jet is deposited on a collector as a result
of the electrostatic field that is provided by a power supply between the spinneret
and the collector and is applied to spinning droplets. As the tiny jet reaches the
collector, an interconnected web of fine sub-micron size fibers are collected on
the collector.
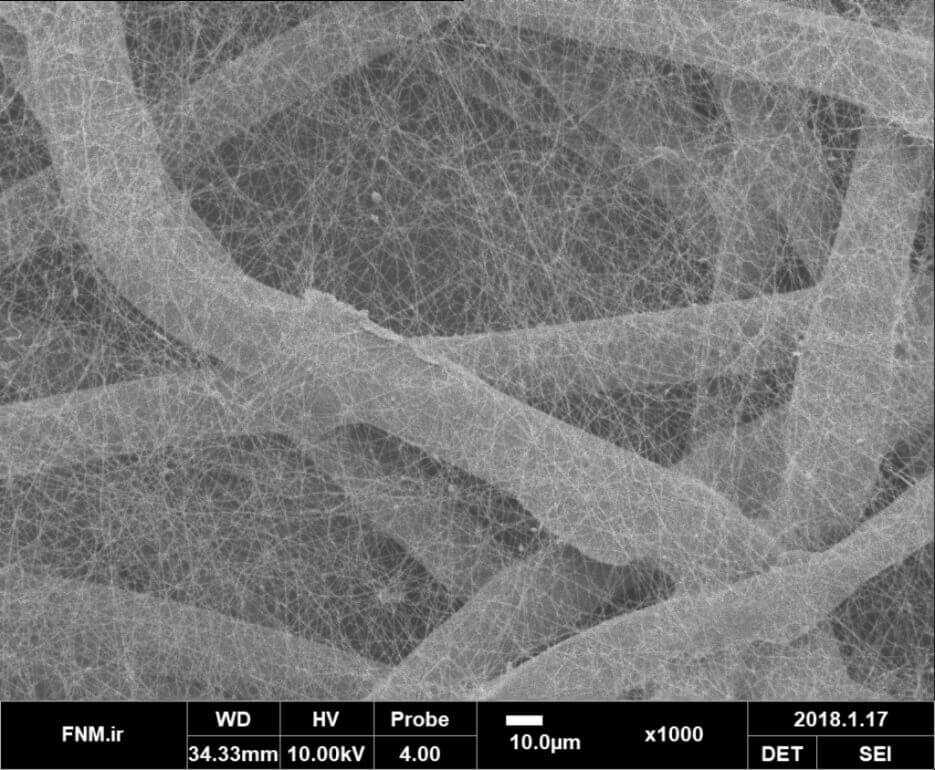
Electrospinning provides
a relatively versatile method of creating a variety of ultrathin fibers (nanofibers).
Nanofibers with some specific properties can be prepared if appropriate solution
or processing parameters are performed. However, electrospinning generally has relatively
low productivity compared to other spinning processes, because the polymer solution
has to be fed at comparatively slow rates and only electrostatic forces are used
to obtain the ultrathin fibers. In order to overcome the aforementioned drawback,
we employed blown electrospinning technique for increasing throughput up to 3 times
compared to conventional electrospinning systems. The combination of the air blowing
force and the electrostatic force is capable of overcoming the high surface tension
of the polymer solution, therefore, the rate of converting solutions to nanofibers
increase significantly. Additionally, the solvent evaporation is accelerated by
blowing air which is a necessary condition for the fiber formation before the jet
reaches the collector during the process. Therefore, many useful polymers, which
previously could not be electrospun, now are processed easily by using the blown
electrospinning process.
FNM’s blown electrospinning machines, which its technique was patented and uses
electric and air blowing forces to produce various nanofibers, can be supplied in
lab, pilot and industrial scales.